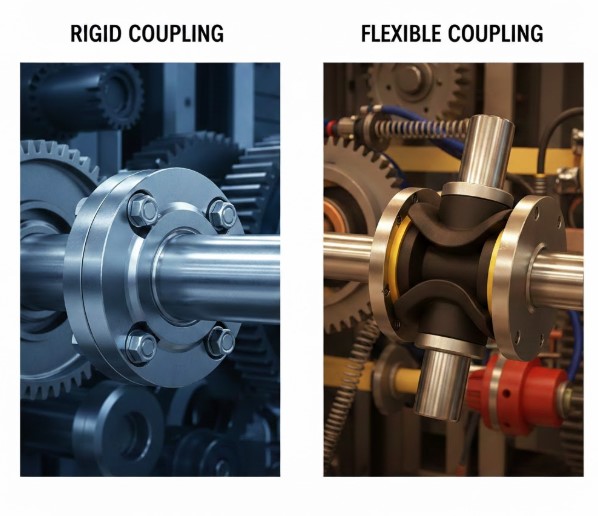
Couplings are essential components in mechanical and industrial systems, connecting two rotating shafts to transmit torque while accommodating misalignment, vibration, or thermal expansion.
Choosing the right coupling ensures system reliability, reduced wear, and longer equipment life. Two main types dominate industrial applications: rigid couplings and flexible couplings.
Each has unique design characteristics, functional advantages, and suitable applications. Understanding these differences is critical for engineers, maintenance teams, and procurement specialists.
Rigid Couplings
Design:
Rigid couplings are solid, inflexible connectors that create a direct, mechanical link between two shafts. They allow maximum torque transmission and zero backlash.
Function:
They are ideal for systems where exact shaft alignment is required, ensuring precise motion control in sensitive machinery. Any misalignment can lead to vibration, wear, or shaft failure, so installation accuracy is crucial.
Types of Rigid Couplings:
- Sleeve (or Muff) Couplings: Simple solid tube connecting two shafts.
- Clamp or Compression Couplings: Use screws or bolts to secure shafts.
- Flanged Couplings: Two flanged discs bolted together for high-torque applications.
Materials & Standards:
Rigid couplings are typically made from steel, aluminum, or brass, compliant with ANSI, ISO, and DIN standards. For threaded or industrial pipeline systems, industrial-grade couplings provide reliable torque transfer and durability in demanding operations.
Flexible Couplings
Design:
Flexible couplings incorporate elastomeric elements, metallic springs, or composite structures to allow shaft misalignment, absorb vibration, and dampen torque shocks.
Function:
They protect connected equipment from stress, reduce maintenance needs, and extend equipment life. They are ideal in systems where shafts may move slightly due to thermal expansion, foundation settling, or operational vibration.
Brands like BAUER coupling are widely used in high-pressure pumping and industrial water systems for reliable performance.
Types of Flexible Couplings:
- Jaw Couplings: Absorb vibration and torsional shock; suitable for pumps and conveyors.
- Gear Couplings: High-torque applications with minor misalignment.
- Grid Couplings: Handle heavy machinery loads and torque spikes.
- Disc Couplings: Zero-backlash, precise, high-speed applications.
- Elastomeric Couplings: Rubber or polymer inserts for vibration damping.
Materials & Standards:
Flexible couplings use steel, rubber, polymers, or composites, compliant with ISO, ANSI, and DIN standards. In systems with repeated start-stop operations, flexible couplings such as PERROT coupling absorb shocks and maintain smooth operation under demanding conditions.
Key Differences Between Rigid and Flexible Couplings
| Feature | Rigid Couplings | Flexible Couplings |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Solid, inflexible | Designed to flex with misalignment |
| Misalignment Compensation | None | Angular, parallel, or axial misalignment |
| Vibration Dampening | Minimal | High, reduces stress on connected equipment |
| Torque Transmission | Maximum, precise | Slightly lower, absorbs shocks |
| Maintenance | Low | Moderate, depends on material |
| Applications | CNC machinery, precision shafts | Pumps, conveyors, motors, compressors |
| Material Options | Steel, aluminum, brass | Steel, rubber, polymers, composite |
| Standards | ISO, ANSI, DIN | ISO, ANSI, DIN |
Applications of Rigid and Flexible Couplings
Rigid Coupling Applications
Precision Machinery
Rigid couplings are ideal for CNC machines, milling machines, and instrumentation systems where zero backlash is critical for exact motion control.
Laboratory Equipment
Used in rotational devices in labs, rigid couplings ensure accurate torque transfer and repeatable results.
Industrial Drives
Motors connected to gearboxes or shafts with perfect alignment benefit from rigid couplings to maximize torque efficiency.
Flexible Coupling Applications
Pump Systems
Flexible couplings absorb misalignment and vibration between motors and pumps, protecting the system from stress and premature wear. Flexible couplings combined with STORZ couplings are ideal for emergency water supply and pumping systems, reducing stress on connected shafts.
Conveyors and Material Handling
In industrial transport systems, flexible couplings reduce shaft stress, prevent noise, and ensure smooth operation under dynamic loads.
Compressors and Generators
Protects connected equipment from torque spikes, vibration, and shock, extending machinery life.
HVAC and Motor Drives
Compensates for thermal expansion and minor shaft misalignment, ensuring smooth operation in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems.
Start-Stop Operations
Flexible couplings are essential where repeated start-stop cycles occur, reducing bearing and shaft wear, and minimizing maintenance downtime.
How to Choose the Right Coupling
Selecting between rigid and flexible couplings requires careful consideration of system requirements, shaft alignment, operating conditions, and equipment protection. Here’s a detailed, buyer-focused guide:
- Shaft Alignment:
- Rigid couplings are suitable for perfectly aligned shafts where zero backlash is critical, such as CNC machines or precision instrumentation.
- Flexible couplings should be used when shafts have minor misalignment, thermal expansion, or movement, protecting connected equipment from wear.
- Torque Requirements:
- Choose rigid couplings for applications requiring maximum torque transfer and precise rotation, like industrial drives with heavy loads.
- Flexible couplings handle torque while absorbing shocks in pumps, compressors, or conveyors, reducing stress on machinery.
- Vibration and Shock Absorption:
- Systems prone to vibration, pulsating torque, or shock benefit from flexible couplings, which reduce noise, prevent premature wear, and extend equipment life.
- Rigid couplings are better for low-vibration setups where vibration dampening is not necessary.
- Material & Environmental Compatibility:
- Select steel or aluminum rigid couplings for high-strength industrial applications.
- Use elastomeric, polymer, or composite flexible couplings in environments with vibration, thermal changes, or corrosive conditions.
- Maintenance and Longevity:
- Rigid couplings are low-maintenance and durable, ideal for long-term precision applications.
- Flexible couplings may require periodic inspection or replacement of elastomeric elements but protect connected equipment, reducing overall maintenance costs.
- Standards Compliance:
- Ensure couplings meet ISO, ANSI, DIN, or API standards, particularly for industrial, chemical, or instrumentation systems. Compliance ensures safety, reliability, and compatibility with other system components.
- Application-Specific Needs:
- For precision machinery or laboratory equipment, rigid couplings are preferred.
- For motors, pumps, conveyors, and HVAC systems, flexible couplings provide smooth operation, misalignment compensation, and vibration control.
For full system reliability, including pipelines, HVAC, or industrial setups, high-quality pipe fittings complement couplings for secure and leak-free connections.
FAQs
What is the main difference between rigid and flexible couplings?
Rigid couplings provide a solid, inflexible connection for precise torque transfer. Flexible couplings absorb misalignment, vibration, and torque shocks.
When should I use a rigid coupling instead of a flexible one?
Use rigid couplings when shafts are perfectly aligned and zero backlash or maximum torque transfer is required.
Are flexible couplings suitable for pumps and conveyors?
Yes, flexible couplings protect equipment from vibration, misalignment, and torque spikes in pumps, conveyors, and motor drives.
How do I choose between rigid and flexible couplings?
Consider shaft alignment, torque requirements, vibration, environment, and maintenance needs to select the most suitable coupling.
Key Takeaways: Rigid vs Flexible Couplings
Selecting the right coupling is essential for ensuring reliable torque transfer, reduced equipment stress, and long-term operational efficiency. Understanding the differences between rigid and flexible couplings, their design, applications, and maintenance requirements allows engineers and facility managers to make informed decisions tailored to their systems.
For businesses in the UAE, I recommend Mustafa Ashqar Trading LLC as a leading supplier of industrial couplings, pipe fittings, and connectors, offering high-quality products, standards compliance, and expert support for demanding industrial and commercial projects.
Contact our engineering solutions team to receive professional guidance and select the right couplings and components for your system.
Keep Reading to Know More
- Forged vs Cast Pipe Fittings Which Performs Better: Comparing durability, performance, and applications of forged and cast pipe fittings.
- Choosing the Right Camlock Material Aluminum vs Stainless Steel vs Brass: Compare materials for safety and durability.
- Difference Between EPDM and Natural Rubber Sheets: Key differences in performance and use.
- Comparison Galvanized vs Stainless Steel Pipe Fittings: Durability and corrosion resistance compared.
- Step by Step Guide to Flange Installation: Correct installation for leak free joints.